Clang-Repl¶
Clang-Repl is an interactive C++ interpreter that allows for incremental compilation. It supports interactive programming for C++ in a read-evaluate-print-loop (REPL) style. It uses Clang as a library to compile the high level programming language into LLVM IR. Then the LLVM IR is executed by the LLVM just-in-time (JIT) infrastructure.
Clang-Repl is suitable for exploratory programming and in places where time to insight is important. Clang-Repl is a project inspired by the work in Cling, a LLVM-based C/C++ interpreter developed by the field of high energy physics and used by the scientific data analysis framework ROOT. Clang-Repl allows to move parts of Cling upstream, making them useful and available to a broader audience.
Clang-Repl Basic Data Flow¶
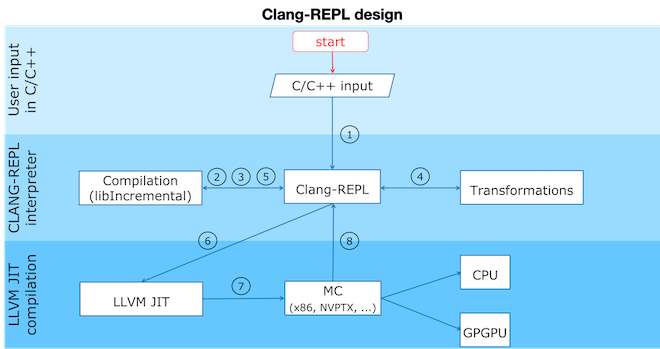
Clang-Repl data flow can be divided into roughly 8 phases:
Clang-Repl controls the input infrastructure by an interactive prompt or by an interface allowing the incremental processing of input.
Then it sends the input to the underlying incremental facilities in Clang infrastructure.
Clang compiles the input into an AST representation.
When required the AST can be further transformed in order to attach specific behavior.
The AST representation is then lowered to LLVM IR.
The LLVM IR is the input format for LLVM’s JIT compilation infrastructure. The tool will instruct the JIT to run specified functions, translating them into machine code targeting the underlying device architecture (eg. Intel x86 or NVPTX).
The LLVM JIT lowers the LLVM IR to machine code.
The machine code is then executed.
Build Instructions:¶
$ cd llvm-project
$ mkdir build
$ cd build
$ cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RelWithDebInfo -DLLVM_ENABLE_PROJECTS=clang -G "Unix Makefiles" ../llvm
Note here, above RelWithDebInfo - Debug / Release
cmake --build . --target clang clang-repl -j n
OR
cmake --build . --target clang clang-repl
Clang-repl is built under llvm-project/build/bin. Proceed into the directory llvm-project/build/bin
./clang-repl
clang-repl>
Clang-Repl Usage¶
Clang-Repl is an interactive C++ interpreter that allows for incremental compilation. It supports interactive programming for C++ in a read-evaluate-print-loop (REPL) style. It uses Clang as a library to compile the high level programming language into LLVM IR. Then the LLVM IR is executed by the LLVM just-in-time (JIT) infrastructure.
Basic:¶
clang-repl> #include <iostream>
clang-repl> int f() { std::cout << "Hello Interpreted World!\n"; return 0; }
clang-repl> auto r = f();
// Prints Hello Interpreted World!
clang-repl> #include<iostream>
clang-repl> using namespace std;
clang-repl> std::cout << "Welcome to CLANG-REPL" << std::endl;
Welcome to CLANG-REPL
// Prints Welcome to CLANG-REPL
Function Definitions and Calls:¶
clang-repl> #include <iostream>
clang-repl> int sum(int a, int b){ return a+b; };
clang-repl> int c = sum(9,10);
clang-repl> std::cout << c << std::endl;
19
clang-repl>
Iterative Structures:¶
clang-repl> #include <iostream>
clang-repl> for (int i = 0;i < 3;i++){ std::cout << i << std::endl;}
0
1
2
clang-repl> while(i < 7){ i++; std::cout << i << std::endl;}
4
5
6
7
Classes and Structures:¶
clang-repl> #include <iostream>
clang-repl> class Rectangle {int width, height; public: void set_values (int,int);\
clang-repl... int area() {return width*height;}};
clang-repl> void Rectangle::set_values (int x, int y) { width = x;height = y;}
clang-repl> int main () { Rectangle rect;rect.set_values (3,4);\
clang-repl... std::cout << "area: " << rect.area() << std::endl;\
clang-repl... return 0;}
clang-repl> main();
area: 12
clang-repl>
// Note: This '\' can be used for continuation of the statements in the next line
Lamdas:¶
clang-repl> #include <iostream>
clang-repl> using namespace std;
clang-repl> auto welcome = []() { std::cout << "Welcome to REPL" << std::endl;};
clang-repl> welcome();
Welcome to REPL
Using Dynamic Library:¶
clang-repl> %lib print.so
clang-repl> #include"print.hpp"
clang-repl> print(9);
9
Generation of dynamic library
// print.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "print.hpp"
void print(int a)
{
std::cout << a << std::endl;
}
// print.hpp
void print (int a);
// Commands
clang++-17 -c -o print.o print.cpp
clang-17 -shared print.o -o print.so
Closure or Termination:¶
clang-repl>%quit
Just like Clang, Clang-Repl can be integrated in existing applications as a library (using the clangInterpreter library). This turns your C++ compiler into a service that can incrementally consume and execute code. The Compiler as A Service (CaaS) concept helps support advanced use cases such as template instantiations on demand and automatic language interoperability. It also helps static languages such as C/C++ become apt for data science.
Comments:¶